Chapter 16 - Urinary System
The urinary system (also known as the renal system) comprises of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and the urethra. Its main function is the production, storage, and expulsion of urine.
KIDNEY
The Kidneys are paired organs that filter blood and produce urine. They are also involved in the regulation of pressure, volume, and pH of blood.
Nephrons are the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each nephron includes a filter, called the renal corpuscle, and a single, long tubule through which the filtrate passes before emerging as urine.
Renal Corpuscle
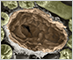
The renal corpuscle contains the filtration apparatus of the nephron. It consists of a glomerulus, which is a tuft of capillaries, and Bowman's capsule which surrounds the glomerulus.
This remarkable micrograph is an exceptionally large montage of an entire renal corpuscle (144 x 134 µm).
Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule that wrap around the capillaries of the glomerulus.
The endothelium of the glomerular capillaries possess numerous fenestrations.
The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three components:
- Endothelium of glomerular capillaries
- Glomerular basement membrane
- Filtration slit diaphragm between pedicels (or foot processes) of podocytes
Renal Tubule
The renal tubules of a nephron consist of a proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule.
Blood Supply
Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive almost 20% of the cardiac output.
URINARY BLADDER
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine, allowing urination to be infrequent and voluntary. It is lined by transitional epithelium (urothelium).